Textbook Question
If a double-stranded DNA molecule is 22% G, what is the percentage of A, T, and C? Explain.
1471
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
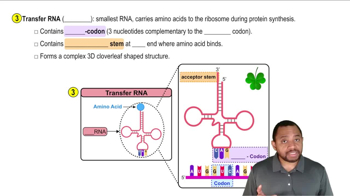


If a double-stranded DNA molecule is 22% G, what is the percentage of A, T, and C? Explain.
How are replication, transcription, and translation similar? How are they different?
Rank the following in order of size: tRNA, DNA, mRNA.
Which amino acid(s) have the most codons?
Look at Table 26.3 and find codons for the following amino acids:
a. Val
If the sequence T-A-C-C-C-T appears on the informational strand of DNA, what sequence appears opposite it on the template strand? Label your answer with 3′ and 5′ ends.