Textbook Question
The DNA from sea urchins contains about 32% A and about 18% G. What percentages of T and C would you expect in sea urchin DNA? Explain.
646
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

The DNA from sea urchins contains about 32% A and about 18% G. What percentages of T and C would you expect in sea urchin DNA? Explain.
If a double-stranded DNA molecule is 22% G, what is the percentage of A, T, and C? Explain.
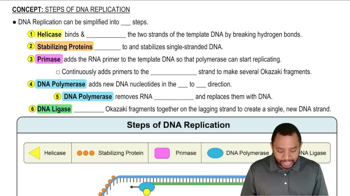
How are replication, transcription, and translation similar? How are they different?
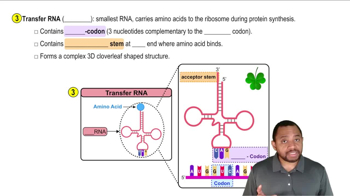
What is an anticodon, and on what kind of nucleic acid is it found?
Which amino acid(s) have the most codons?
Look at Table 26.3 and find codons for the following amino acids:
a. Val