Textbook Question
Is a DNA molecule neutral, negatively charged, or positively charged? Explain.
1040
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

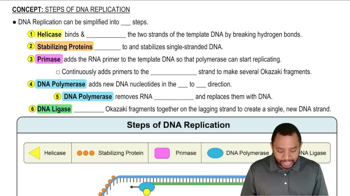

Is a DNA molecule neutral, negatively charged, or positively charged? Explain.
DNA and RNA, like proteins, can be denatured to produce unfolded or uncoiled strands. Heating DNA to what is referred to as its “melting temperature” denatures it (the two strands of the double helix become separated). Why does a longer strand of DNA have a higher melting temperature than a shorter one?
What are Okazaki fragments? What role do they serve in DNA metabolism?
What is the function of the spliceosome in hnRNA?
What mRNA base sequences are complementary to the following DNA template sequences? Be sure to label the 5′ and 3′ ends of the complementary sequences.
a. 5′ CAT GCT CTA CAG 3′
List possible codon sequences for the following amino acids.
a. Val