Textbook Question
Write the IUPAC and common names, if any, for each of the following amides:
c.
719
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


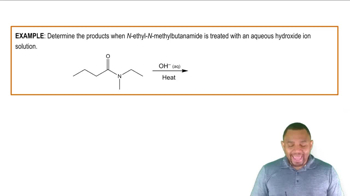
Write the IUPAC and common names, if any, for each of the following amides:
c.
Draw the condensed structural formula for a and b and the line-angle formula for c and d:
b. 2-methylpentanamide
Draw the condensed structural formula for a and b and the line-angle formula for c and d:
a. heptanamide
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the hydrolysis of each of the following amides with HCl:
b.
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the hydrolysis of each of the following amides with HCl:
d.
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the hydrolysis of each of the following amides with NaOH:
a.