Use Lewis symbols to determine the formula for the compound that forms between each pair of elements. a. Ca and N b. Mg and I c. Ca and S d. Cs and F
Ch.9 - Chemical Bonding I: The Lewis Model

Chapter 9, Problem 45
The lattice energy of CsF is -744 kJ/mol, whereas that of BaO is -3029 kJ/mol. Explain this large difference in lattice energy.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Lattice energy is the energy required to separate one mole of an ionic solid into its gaseous ions. It is influenced by the charges of the ions and the distance between them.
CsF consists of Cs^+ and F^- ions, while BaO consists of Ba^2+ and O^2- ions. The charges on the ions in BaO are higher than those in CsF.
According to Coulomb's Law, the lattice energy is directly proportional to the product of the charges of the ions. Therefore, the higher charges in BaO result in a greater lattice energy.
The size of the ions also affects lattice energy. Smaller ions can get closer together, increasing the lattice energy. Ba^2+ and O^2- are smaller than Cs^+ and F^-, contributing to the higher lattice energy of BaO.
In summary, the large difference in lattice energy between CsF and BaO is due to the higher ionic charges and smaller ionic radii in BaO, leading to stronger electrostatic attractions.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lattice Energy
Lattice energy is the amount of energy released when gaseous ions combine to form an ionic solid. It is a measure of the strength of the forces between the ions in an ionic compound. Higher lattice energy indicates stronger ionic bonds, which typically results from greater charges on the ions and smaller ionic radii.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lattice Energy
Ionic Charge
The charge of the ions significantly influences lattice energy. In the case of CsF, cesium (Cs) has a +1 charge and fluoride (F) has a -1 charge, resulting in a relatively lower lattice energy. In contrast, BaO consists of barium (Ba) with a +2 charge and oxide (O) with a -2 charge, leading to a stronger electrostatic attraction and thus a higher lattice energy.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Formal Charge
Ionic Radius
The size of the ions, or ionic radius, also affects lattice energy. Smaller ions can pack more closely together, increasing the electrostatic attraction between them. In BaO, the smaller size of the oxide ion compared to the fluoride ion in CsF contributes to the larger lattice energy, as the closer proximity of the ions enhances the overall stability of the ionic lattice.
Recommended video:
Guided course
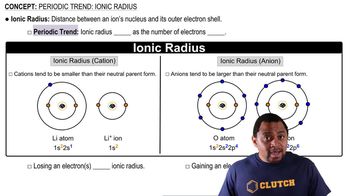
Ionic Radius
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1733
views
Textbook Question
Rubidium iodide has a lattice energy of -617 kJ/mol, while potassium bromide has a lattice energy of -671 kJ/mol. Why is the lattice energy of potassium bromide more exothermic than the lattice energy of rubidium iodide?
1490
views
Textbook Question
Use the Born–Haber cycle and data from Appendix IIB, Chapter 8 and this chapter to calculate the lattice energy of KCl. (ΔHsub for potassium is 89.0 kJ/mol.)
850
views
1
rank
2
comments
Textbook Question
Use the Born–Haber cycle and data from Appendix IIB and Table 9.3 to calculate the lattice energy of CaO. (ΔHsub for calcium is 178 kJ/mol; IE1 and IE2 for calcium are 590 kJ/mol and 1145 kJ/mol, respectively; EA1 and EA2 for O are -141 kJ/mol and 744 kJ/mol, respectively.)
2606
views
2
comments
