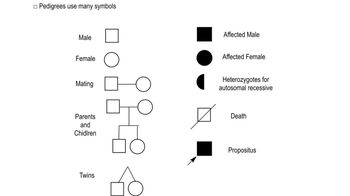
A couple and some of their relatives are screened for Gaucher disease in a community-based screening program. The woman is homozygous for the dominant allele, represented by G. The woman's father, sister, and paternal grandmother are heterozygous carriers of the mutant allele, represented by g. Her paternal grandfather, her mother, and both of her mother's parents are homozygous for the dominant allele. The man is heterozygous and he has a brother with Gaucher disease. The man's parents and grandparents have not been tested, but it is known that none of them has Gaucher disease.
On the pedigree, write the genotypes (GG, Gg, or gg) for each person who has been tested or for whom you can deduce a genotype. If a genotype cannot be determined completely, list the alleles you know or deduce must be present.