Textbook Question
From the following list, identify the types of chromosome changes you expect to show phenotypic consequences.
Interstitial deletion
415
views

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 10 - Eukaryotic Chromosome Abnormalities and Molecular Organization
Ch. 10 - Eukaryotic Chromosome Abnormalities and Molecular Organization Problem 7f
Problem 7f Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

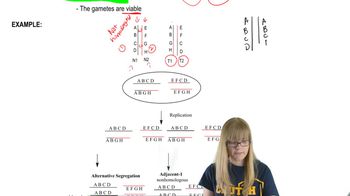

From the following list, identify the types of chromosome changes you expect to show phenotypic consequences.
Interstitial deletion
From the following list, identify the types of chromosome changes you expect to show phenotypic consequences.
Terminal deletion
From the following list, identify the types of chromosome changes you expect to show phenotypic consequences.
Trisomy
From the following list, identify the types of chromosome changes you expect to show phenotypic consequences.
Paracentric inversion
From the following list, identify the types of chromosome changes you expect to show phenotypic consequences.
Monosomy
From the following list, identify the types of chromosome changes you expect to show phenotypic consequences.
Polyploidy