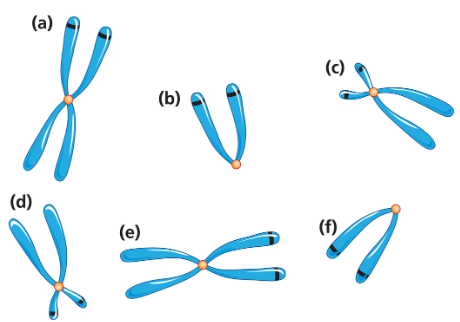
A small population of deer living on an isolated island is separated for many generations from a mainland deer population. The populations retain the same number of chromosomes but hybrids are infertile. One chromosome (shown here) has a different banding pattern in the island population than in the mainland population.
In a mainland–island hybrid deer, recombination takes place in band q1 of the homologous chromosomes. Draw the gametes that result from this event.