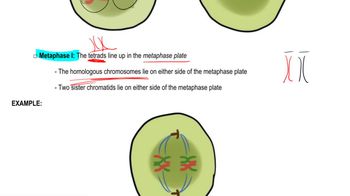
A researcher interested in studying a human gene on chromosome 21 and another gene on the X chromosome uses FISH probes to locate each gene. The chromosome 21 probe produces green fluorescent color, and the X chromosome probe produces red fluorescent color.
If the subject studied is male, how many green and red spots will be detected? Explain your answer.