Experiments by Charles Yanofsky in the 1950s and 1960s helped characterize the nature of tryptophan synthesis in E. coli. In one of Yanofsky's experiments, he identified glycine (Gly) as the wild-type amino acid in position 211 of tryptophan synthetase, the product of the trpA gene. He identified two independent missense mutants with defective tryptophan synthetase at these positions that resulted from base-pair substitutions. One mutant encoded arginine (Arg) and another encoded glutamic acid (Glu). At position 235, wild-type tryptophan synthetase contains serine (Ser) but a base-pair substitution mutant encodes leucine (Leu). At position 243, the wild-type polypeptide contains glutamine and a base-pair substitution mutant encodes a stop codon. Identify the most likely wild-type codons for positions 211, 235, and 243. Justify your answer in each case.

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 11 - Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Homologous Recombination
Ch. 11 - Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Homologous Recombination Problem 32c
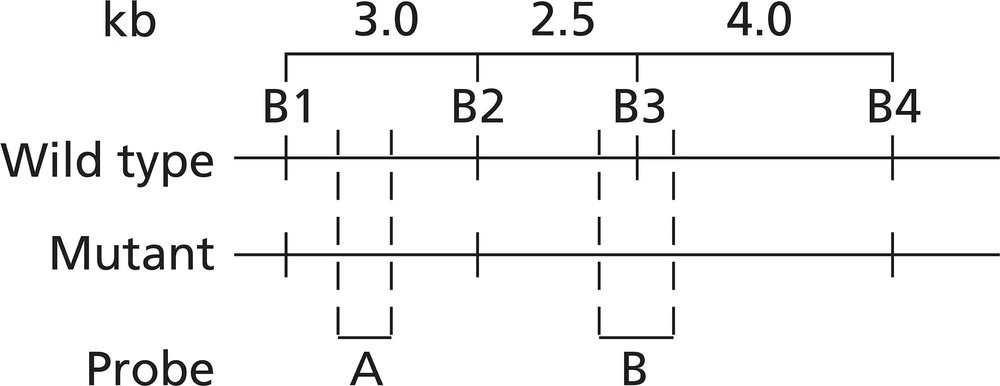
Problem 32cAlkaptonuria is a human autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutation of the HAO gene that encodes the enzyme homogentisic acid oxidase. A map of the HAO gene region reveals four BamHI restriction sites (B1 to B4) in the wild-type allele and three BamHI restriction sites in the mutant allele. BamHI utilizes the restriction sequence 5′-GGATCC-3′. The BamHI restriction sequence identified as B3 is altered to 5′-GGAACC-3′ in the mutant allele. The mutation results in a Ser-to-Thr missense mutation. Restriction maps of the two alleles are shown below, and the binding sites of two molecular probes (probe A and probe B) are identified.
DNA samples taken from a mother (M), father (F), and two children (C1 and C2) are analyzed by Southern blotting of BamHI-digested DNA. The gel electrophoresis results are illustrated.

Explain how the DNA sequence change results in a Ser-to-Thr missense mutation.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Missense Mutation

Restriction Enzymes and Sites

Southern Blotting

Alkaptonuria is a human autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutation of the HAO gene that encodes the enzyme homogentisic acid oxidase. A map of the HAO gene region reveals four BamHI restriction sites (B1 to B4) in the wild-type allele and three BamHI restriction sites in the mutant allele. BamHI utilizes the restriction sequence 5′-GGATCC-3′. The BamHI restriction sequence identified as B3 is altered to 5′-GGAACC-3′ in the mutant allele. The mutation results in a Ser-to-Thr missense mutation. Restriction maps of the two alleles are shown below, and the binding sites of two molecular probes (probe A and probe B) are identified.
DNA samples taken from a mother (M), father (F), and two children (C1 and C2) are analyzed by Southern blotting of BamHI-digested DNA. The gel electrophoresis results are illustrated.
Using A to represent the wild-type allele and a for the mutant allele, identify the genotype of each family member. Identify any family member who is alkaptonuric.
Alkaptonuria is a human autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutation of the HAO gene that encodes the enzyme homogentisic acid oxidase. A map of the HAO gene region reveals four BamHI restriction sites (B1 to B4) in the wild-type allele and three BamHI restriction sites in the mutant allele. BamHI utilizes the restriction sequence 5′-GGATCC-3′. The BamHI restriction sequence identified as B3 is altered to 5′-GGAACC-3′ in the mutant allele. The mutation results in a Ser-to-Thr missense mutation. Restriction maps of the two alleles are shown below, and the binding sites of two molecular probes (probe A and probe B) are identified.
DNA samples taken from a mother (M), father (F), and two children (C1 and C2) are analyzed by Southern blotting of BamHI-digested DNA. The gel electrophoresis results are illustrated.
In a separate figure, draw the gel electrophoresis band patterns for all the genotypes that could be found in children of this couple.
In an experiment employing the methods of the Ames test, two strains of Salmonella are used. Strain A contains a base-substitution mutation, and Strain B contains a frameshift mutation. Four plates are prepared to test the mutagenicity of the compound ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS). Plate 1 is a control plate with Strain A and S9 extract but no EMS. Plate 2 is also a control plate and contains Strain B and S9 extract but no EMS. Plate 3 contains Strain A along with S9 extract and EMS, and Plate 4 contains Strain B, S9 extract, and EMS.
Characterize the expected distribution of colony growth on the four plates. Defend your growth prediction for each plate.
In an experiment employing the methods of the Ames test, two strains of Salmonella are used. Strain A contains a base-substitution mutation, and Strain B contains a frameshift mutation. Four plates are prepared to test the mutagenicity of the compound ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS). Plate 1 is a control plate with Strain A and S9 extract but no EMS. Plate 2 is also a control plate and contains Strain B and S9 extract but no EMS. Plate 3 contains Strain A along with S9 extract and EMS, and Plate 4 contains Strain B, S9 extract, and EMS.
What event is being detected by growth of a colony on any of the four plates?
In an experiment employing the methods of the Ames test, two strains of Salmonella are used. Strain A contains a base-substitution mutation, and Strain B contains a frameshift mutation. Four plates are prepared to test the mutagenicity of the compound ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS). Plate 1 is a control plate with Strain A and S9 extract but no EMS. Plate 2 is also a control plate and contains Strain B and S9 extract but no EMS. Plate 3 contains Strain A along with S9 extract and EMS, and Plate 4 contains Strain B, S9 extract, and EMS.
Why is the S9 extract added to each of the plates?