If two six-sided dice are rolled, what is the probability that the total number of spots showing is
an odd number?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



If two six-sided dice are rolled, what is the probability that the total number of spots showing is
an odd number?
Experimental Insight 2.1 describes data, collected by a genetics class like yours, on the numbers of kernels of different colors in bicolor corn. To test the hypothesis that the presence of kernels of different colors in each ear is the result of the segregation of two alleles of a single gene, the class counted 12,356 kernels and found that 9304 were yellow and 3052 were white. Use chi-square analysis to evaluate the fit between the segregation hypothesis and the class results.
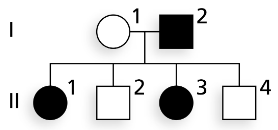
The accompanying pedigree shows the transmission of a phenotypic character. Using B to represent a dominant allele and b to represent a recessive allele,
Give the genotype(s) possible for each member of the family, assuming the trait is autosomal dominant.
The seeds in bush bean pods are each the product of an independent fertilization event. Green seed color is dominant to white seed color in bush beans. If a heterozygous plant with green seeds self-fertilizes, what is the probability that 6 seeds in a single pod of the progeny plant will consist of 3 green and 3 white seeds?
The seeds in bush bean pods are each the product of an independent fertilization event. Green seed color is dominant to white seed color in bush beans. If a heterozygous plant with green seeds self-fertilizes, what is the probability that 6 seeds in a single pod of the progeny plant will consist of all green seeds?
The seeds in bush bean pods are each the product of an independent fertilization event. Green seed color is dominant to white seed color in bush beans. If a heterozygous plant with green seeds self-fertilizes, what is the probability that 6 seeds in a single pod of the progeny plant will consist of at least 1 white seed?