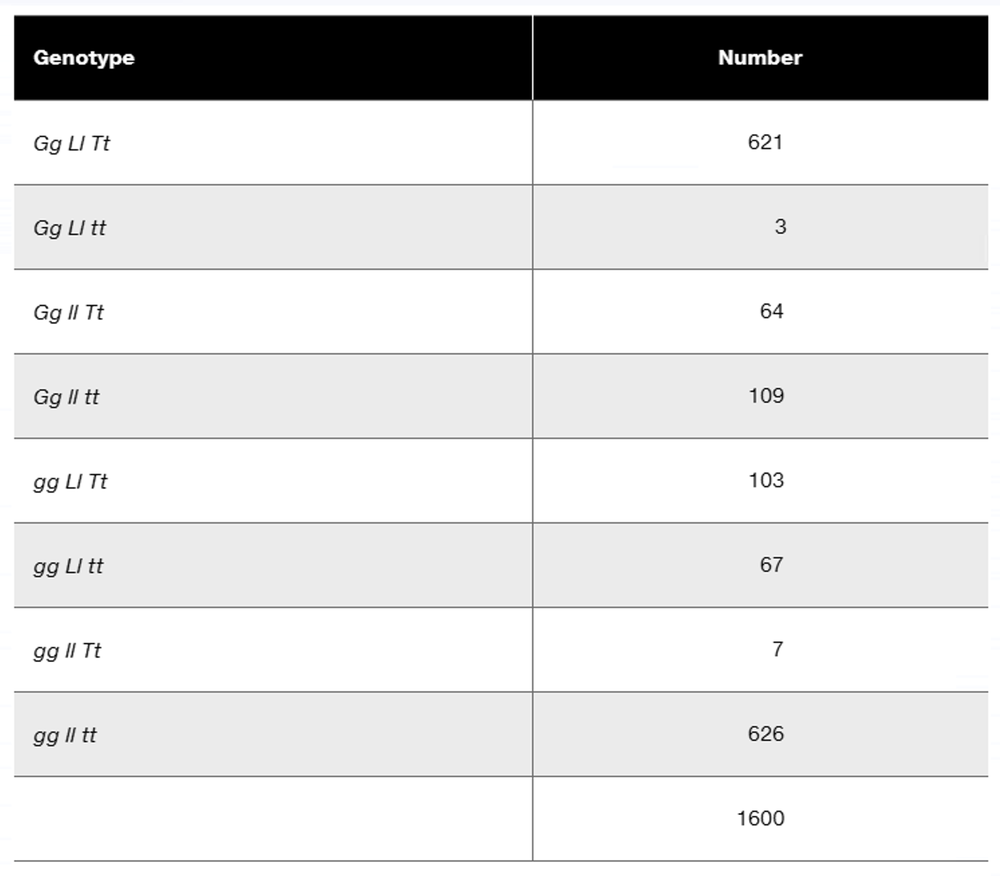
Three dominant traits of corn seedlings, tunicate seed (T-), glossy appearance (G-), and liguled stem (L-), are studied along with their recessive counterparts, nontunicate (tt), nonglossy (gg), and liguleless (ll). A trihybrid plant with the three dominant traits is crossed to a nontunicate, nonglossy, liguleless plant. Kernels on ears of progeny plants are scored for the traits, with the following results:
If evidence of linkage is present, calculate the recombination frequency or frequencies from the data presented.