In a diploid plant species, an F₁ with the genotype Gg Ll Tt is test-crossed to a pure-breeding recessive plant with the genotype gg ll tt. The offspring genotypes are as follows:
Explain the meaning of this I value.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



In a diploid plant species, an F₁ with the genotype Gg Ll Tt is test-crossed to a pure-breeding recessive plant with the genotype gg ll tt. The offspring genotypes are as follows:
Explain the meaning of this I value.
The table given here lists the arrangement of alleles of linked genes in dihybrid organisms, the recombination frequency between the genes, and specific gamete genotypes. Using the information provided, determine the expected frequency of the listed gametes. Assume one map unit equals 1% recombination and, when three genes are involved, interference is zero.
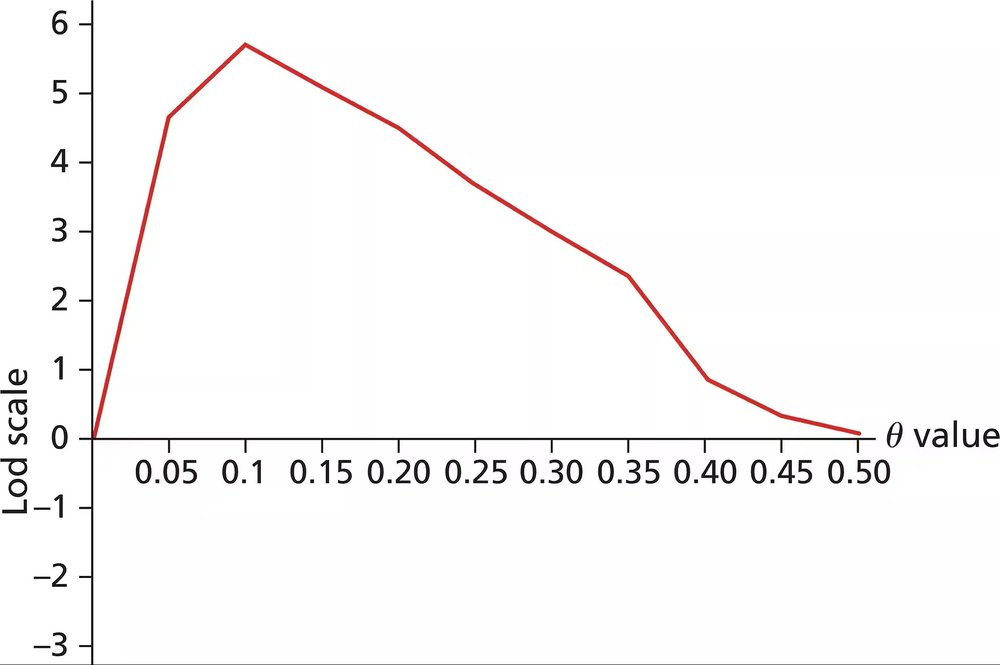
The Rh blood group in humans is determined by a gene on chromosome 1. A dominant allele produces Rh+ blood type, and a recessive allele generates Rh-. Elliptocytosis is an autosomal dominant disorder that produces abnormally shaped red blood cells that have a short life span resulting in hereditary anemia. A large family with elliptocytosis is tested for genetic linkage of Rh blood group and the disease. The lod score data below are obtained for the family.
From these data, can you conclude that Rh and elliptocytosis loci are genetically linked in this family? Why or why not?
The Rh blood group in humans is determined by a gene on chromosome 1. A dominant allele produces Rh+ blood type, and a recessive allele generates Rh-. Elliptocytosis is an autosomal dominant disorder that produces abnormally shaped red blood cells that have a short life span resulting in hereditary anemia. A large family with elliptocytosis is tested for genetic linkage of Rh blood group and the disease. The lod score data below are obtained for the family.
Over what range of θ do lod scores indicate significant evidence in favor of genetic linkage?
Genetic linkage mapping for a large number of families identifies 4% recombination between the genes for Rh blood type and elliptocytosis (see Problem 18). At the Rh locus, alleles R and r control Rh+ and Rh- blood types. Allele E producing elliptocytosis is dominant to the wild-type recessive allele e. Tom and Terri each have elliptocytosis, and each is . Tom's mother has elliptocytosis and is Rh- while his father is healthy and has Rh+. Terri's father is Rh+ and has elliptocytosis; Terri's mother is Rh- and is healthy.
What is the probability that the first child of Tom and Terri will be Rh− and have elliptocytosis?
Genetic linkage mapping for a large number of families identifies 4% recombination between the genes for Rh blood type and elliptocytosis (see Problem 18). At the Rh locus, alleles R and r control Rh+ and Rh- blood types. Allele E producing elliptocytosis is dominant to the wild-type recessive allele e. Tom and Terri each have elliptocytosis, and each is . Tom's mother has elliptocytosis and is Rh- while his father is healthy and has Rh+. Terri's father is Rh+ and has elliptocytosis; Terri's mother is Rh- and is healthy.
What is the probability that a child of Tom and Terri who is Rh+ will have elliptocytosis?