Suppose you have a 1-kb segment of cloned DNA that is suspected to contain a eukaryotic promoter, including a TATA box, a CAAT box, and an upstream GC-rich sequence. The clone also contains a gene whose transcript is readily detectable. Your laboratory supervisor asks you to outline an experiment that will (1) determine if eukaryotic transcription factors (TF) bind to the fragment and, if so, (2) identify where on the fragment the transcription factors bind. All necessary reagents, equipment, and experimental know-how are available in the laboratory. Your assignment is to propose techniques to be used to address the two items your supervisor has listed and to describe the kind of results that would indicate binding of TF to the DNA and the location of the binding.

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 8 - Molecular Biology of Transcription and RNA Processing
Ch. 8 - Molecular Biology of Transcription and RNA Processing Problem 28c
Problem 28cAssume that a mutation affects the gene for each of the following eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Match each mutation with the possible effects from the list provided. More than one effect is possible for each mutation.
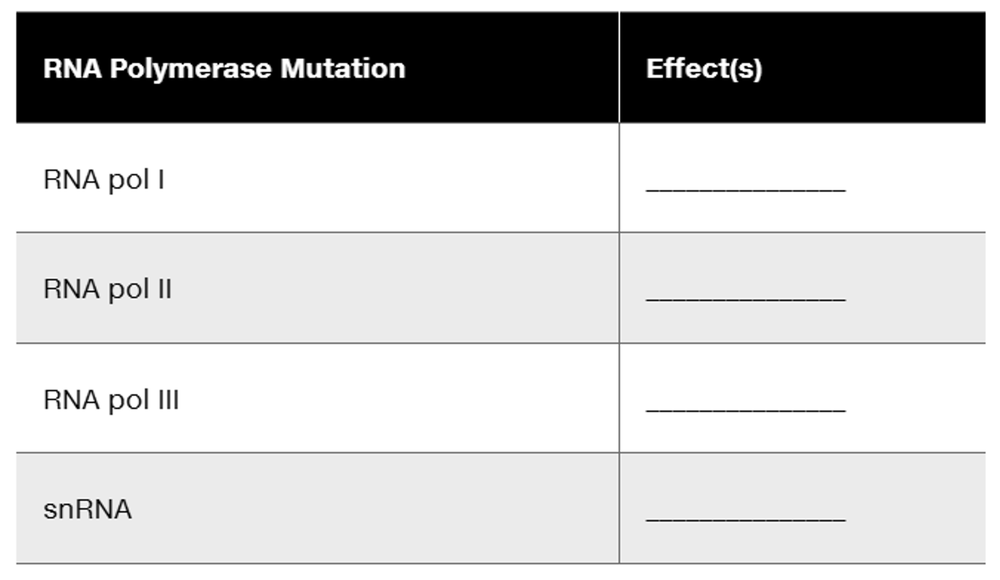
Some rRNA is not synthesized.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Eukaryotic RNA Polymerases
Mutations and Their Effects

snRNA and Its Role
Assume that a mutation affects the gene for each of the following eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Match each mutation with the possible effects from the list provided. More than one effect is possible for each mutation.
Pre-mRNA does not have introns removed.
Assume that a mutation affects the gene for each of the following eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Match each mutation with the possible effects from the list provided. More than one effect is possible for each mutation.
Some pre-mRNA is not synthesized.
Assume that a mutation affects the gene for each of the following eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Match each mutation with the possible effects from the list provided. More than one effect is possible for each mutation.
Some tRNA is not synthesized.
Assume that a mutation affects the gene for each of the following eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Match each mutation with the possible effects from the list provided. More than one effect is possible for each mutation.
Ribosomal RNA is not processed.
The DNA sequence below gives the first 12 base pairs of the transcribed region of a gene, and the template and nontemplate strands of DNA are identified. The transcription start is the thymine nucleotide at the end of the sequence given. Use the diagram to answer the list of questions. Make a copy of the diagram before you begin answering the questions, or have one group member diagram the answers for bacteria and another group member diagram the answers for eukaryotes.
Nontemplate strand ___________ TTGCTACGGTCA___________
Template strand ___________ AACGATGCCAGT___________
Write the polarity of the two DNA strands shown.
