Do the amino acids that are in the active site of an enzyme have to be near each other in the enzyme’s primary structure? If no, explain.

What type of interactions between an enzyme and its substrate help to stabilize ES?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
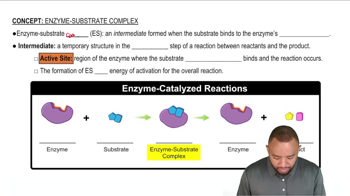
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
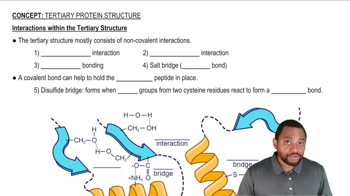
Binding Interactions
Induced Fit Model
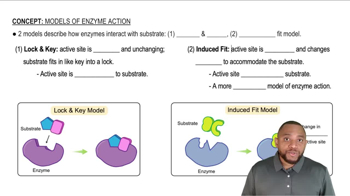
The enzyme trypsin catalyzes the breakdown of many structurally diverse proteins in foods. Does the induced-fit or lock-and-key model explain the action of trypsin better? Explain.
The enzyme sucrase catalyzes the hydrolysis of the disaccharide sucrose but not the disaccharide lactose. Does the induced-fit or lock-and-key model explain the action of sucrase better? Explain.
Does each of the following statements describe a simple enzyme (no cofactor or coenzyme necessary), an enzyme that requires a cofactor, or an enzyme that requires a coenzyme?
b. consists of one polypeptide chain in its active form
Does each of the following statements describe a simple enzyme (no cofactor or coenzyme necessary), an enzyme that requires a cofactor, or an enzyme that requires a coenzyme?
c. contains vitamin B6 in its active site
A substrate is held in the active site of an enzyme by attractive forces between the substrate and the amino acid side chains. For the outlined regions A, B, and C on the following substrate molecule:
b. Could the amino acids serine, lysine, or glutamate be present in the active site? Support your answer.
