Textbook Question
Identify all the functional groups present in the following:
(a)
719
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

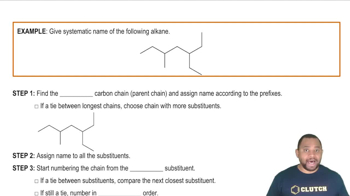

Identify all the functional groups present in the following:
(a)
The most prevalent fatty acid in coconut oil is lauric acid, a saturated fatty acid containing 12 carbons. Draw lauric acid in skeletal structure.
Draw the condensed structural formula for each of the following alkyl groups:
(b) methyl
Draw the skeletal structure for each of the following compounds:
(a) 2,3-dimethylpentane
Draw the skeletal structure for each of the following compounds:
(a) 3-ethylhexane
Give the correct IUPAC name for each of the following compounds:
(a)