Textbook Question
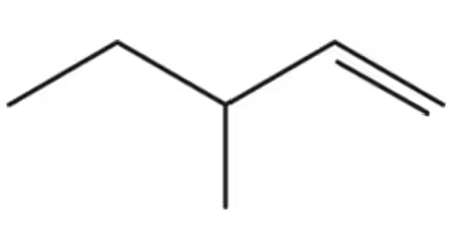
Convert the condensed structures shown to skeletal structures.
(b) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
634
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Convert the condensed structures shown to skeletal structures.
(b) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
Convert the skeletal structures shown to condensed structures.
(a)
Convert the skeletal structures shown to condensed structures.
(b)
Alkanes are also referred to as saturated hydrocarbons. Explain the meaning of the term hydrocarbon. Why are alkanes called saturated hydrocarbons?
Give the skeletal structure and name of the straight-chain alkanes whose molecular formula is shown.
(a) C3H8
Give the skeletal structure and name of the straight-chain alkanes whose molecular formula is shown.
(b) C10H22