Textbook Question
Draw the complete structure of uridine 5′- phosphate, one of the four major ribonucleotides.
886
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Draw the complete structure of uridine 5′- phosphate, one of the four major ribonucleotides.
Draw the complete structure of the RNA dinucleotide U-C. Identify the 5′ and 3′ ends of the dinucleotide.
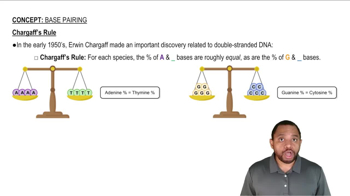
What is meant by the term base pairing?
The DNA from sea urchins contains about 32% A and about 18% G. What percentages of T and C would you expect in sea urchin DNA? Explain.
If a double-stranded DNA molecule is 22% G, what is the percentage of A, T, and C? Explain.
How are replication, transcription, and translation similar? How are they different?