Textbook Question
What are the two structural types of bases in DNA and RNA? Which bases correspond to each type?
770
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

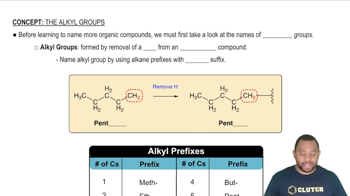
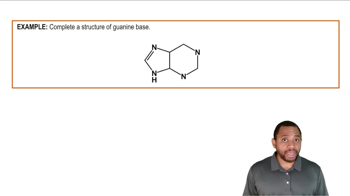
What are the two structural types of bases in DNA and RNA? Which bases correspond to each type?
What is the difference between the 3′ end and the 5′ end of a polynucleotide?
Are polynucleotides synthesized 3′ to 5′ or 5′ to 3′?
Draw the complete structure of the RNA dinucleotide U-C. Identify the 5′ and 3′ ends of the dinucleotide.
What is meant by the term base pairing?
What does it mean to speak of bases as being complementary?