What amino acids do the following sequences code for?
a. AUC

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



What amino acids do the following sequences code for?
a. AUC
What amino acid sequence is coded for by the mRNA base sequence CUC-AUU-CCA-UGC-GAC-GUA?
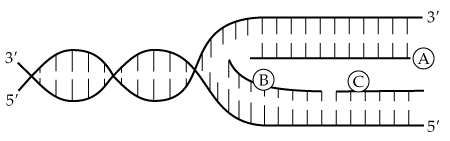
Copy the diagram and use dotted lines to indicate where hydrogen bonding occurs between the complementary strands of DNA. What is the sequence of each strand of DNA drawn (remember that the sequence is written from the 5′ to 3′ end)?
Gln-His-Pro-Gly is the sequence of a molecule known as progenitor thyrotropin-releasing hormone (pro-TRH). If we were searching for pro-TRH genes, we would need to know what sequence of bases in DNA we should be looking for. Use the following boxes to indicate answers to parts (a)–(d).
a. What RNA sequence could code for these four amino acids?
What is the difference between a gene and a chromosome?
What are the two major components of chromatin?