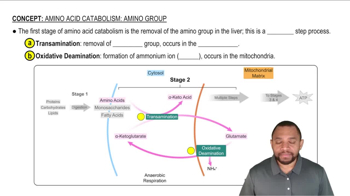
Provide the three-letter amino acid sequence expected from each of the following mRNA segments:
b. 5'CUA|AGC|UUC|AAC|UGG3'

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Provide the three-letter amino acid sequence expected from each of the following mRNA segments:
b. 5'CUA|AGC|UUC|AAC|UGG3'
What is the one-letter amino acid sequence formed from the following mRNA that codes for a pentapeptide that is an endorphin called Met-enkephalin?
5'AUG|UAC|GGU|GGA|UUU|AUG|UAA3'
What is the anticodon on tRNA for each of the following codons in an mRNA?
c. GAA
In sickle-cell anemia, a base substitution in the hemoglobin gene replaces glutamate (a polar amino acid) with valine. Why does the replacement of one amino acid cause such a drastic change in biological function?
A base substitution for an enzyme replaces leucine (a nonpolar amino acid) with alanine. Why does this change in amino acids have little effect on the biological activity of the enzyme?
Provide a reason why there is no vaccine for the common cold.