For each of the following reagents, decide whether chlorobenzene will react with it or not, and, if it does, draw and name the products expected from the reaction.
c. HNO3 and H2SO4 catalyst

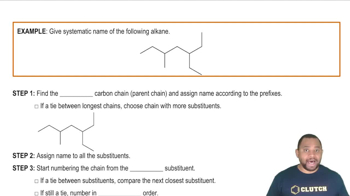
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


For each of the following reagents, decide whether chlorobenzene will react with it or not, and, if it does, draw and name the products expected from the reaction.
c. HNO3 and H2SO4 catalyst
Aromatic compounds do not normally react with hydrogen in the presence of a palladium catalyst but will if very high pressures (200 atm) and high temperatures are used. Under these conditions, toluene adds three molecules of H2 to give an alkane addition product. What is a likely structure for the product?
The explosive trinitrotoluene (TNT) is made by carrying out three successive nitration reactions on toluene. If these nitrations only occur in the ortho and para positions relative to the methyl group, what is the structure of TNT?
Assume that you have two unlabeled bottles, one with cyclohexane and one with cyclohexene. How could you tell them apart by carrying out chemical reactions?
Cinnamaldehyde, the pleasant-smelling substance found in cinnamon oil, has the following structure:
What products would you expect to obtain from reaction of cinnamaldehyde with water and sulfuric acid catalyst?
Predict the products of the following reactions:
e.