The explosive trinitrotoluene (TNT) is made by carrying out three successive nitration reactions on toluene. If these nitrations only occur in the ortho and para positions relative to the methyl group, what is the structure of TNT?

Cinnamaldehyde, the pleasant-smelling substance found in cinnamon oil, has the following structure:
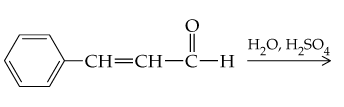
What products would you expect to obtain from reaction of cinnamaldehyde with water and sulfuric acid catalyst?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Cinnamaldehyde Structure and Reactivity

Hydration Reaction
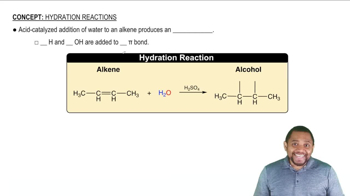
Role of Sulfuric Acid as a Catalyst
The following names are incorrect by IUPAC rules. Draw the structures represented by the following names, and write their correct names. Label each as being symmetrically or unsymmetrically substituted.
a. 2-Methyl-4-hexene
b. 1,3-Dimethyl-1-hexyne
Assume that you have two unlabeled bottles, one with cyclohexane and one with cyclohexene. How could you tell them apart by carrying out chemical reactions?
Predict the products of the following reactions:
e.
Ocimene, a compound isolated from the herb basil, has three double bonds and the IUPAC name 3,7-dimethyl-1, 3-6-octatriene.
b. Draw the structure of the compound formed if enough HBr is added to react with all the double bonds in ocimene.
Which of the following compounds are capable of cis–trans isomerism?
a.
b.
c.
