Indicate what type(s) of intermolecular forces are disrupted and what level of protein structure is changed by the following denaturing treatments:
c. egg whites whipped in a mixing bowl to make meringue

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Indicate what type(s) of intermolecular forces are disrupted and what level of protein structure is changed by the following denaturing treatments:
c. egg whites whipped in a mixing bowl to make meringue
Describe the changes that occur in the primary structure when a protein is denatured versus when a protein is hydrolyzed.
Collagen contains an amino acid that is a modified form of the naturally occurring amino acid.
a. Name the natural amino acid.
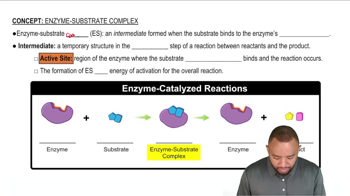
Match the terms (2) enzyme with the following descriptions:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate
b. is the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
c. has a structure that fits the active site of an enzyme
Match the terms (3) substrate with the following descriptions:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate
b. is the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
c. has a structure that fits the active site of an enzyme
Match the terms (1) active site, (2) lock-and-key model, and (3) induced-fit model with the following descriptions:
a. the portion of an enzyme where catalytic activity occurs
b. the active site adapts to the shape of a substrate
c. the active site has a rigid shape