Describe the changes that occur in the primary structure when a protein is denatured versus when a protein is hydrolyzed.

Match the terms (2) enzyme with the following descriptions:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate
b. is the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
c. has a structure that fits the active site of an enzyme
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
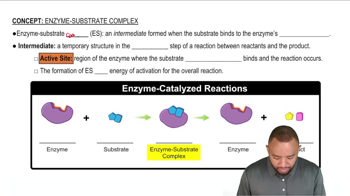
Enzyme Structure

Active Site

Enzyme-Substrate Complex
Collagen contains an amino acid that is a modified form of the naturally occurring amino acid.
a. Name the natural amino acid.
Match the terms (1) ES with the following descriptions:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate
b. is the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
c. has a structure that fits the active site of an enzyme
Match the terms (3) substrate with the following descriptions:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate
b. is the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
c. has a structure that fits the active site of an enzyme
Match the terms (1) active site, (2) lock-and-key model, and (3) induced-fit model with the following descriptions:
a. the portion of an enzyme where catalytic activity occurs
b. the active site adapts to the shape of a substrate
c. the active site has a rigid shape
Do the amino acids that are in the active site of an enzyme have to be near each other in the enzyme’s primary structure? If no, explain.
