Collagen contains an amino acid that is a modified form of the naturally occurring amino acid.
a. Name the natural amino acid.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Collagen contains an amino acid that is a modified form of the naturally occurring amino acid.
a. Name the natural amino acid.
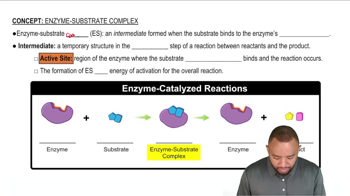
Match the terms (1) ES with the following descriptions:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate
b. is the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
c. has a structure that fits the active site of an enzyme
Match the terms (2) enzyme with the following descriptions:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate
b. is the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
c. has a structure that fits the active site of an enzyme
Match the terms (1) active site, (2) lock-and-key model, and (3) induced-fit model with the following descriptions:
a. the portion of an enzyme where catalytic activity occurs
b. the active site adapts to the shape of a substrate
c. the active site has a rigid shape
Do the amino acids that are in the active site of an enzyme have to be near each other in the enzyme’s primary structure? If no, explain.
The enzyme trypsin catalyzes the breakdown of many structurally diverse proteins in foods. Does the induced-fit or lock-and-key model explain the action of trypsin better? Explain.