Textbook Question
Provide the products for each of the following condensation reactions:
b.
898
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
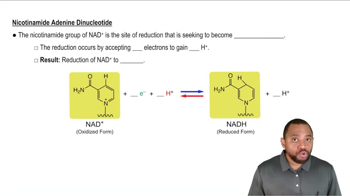
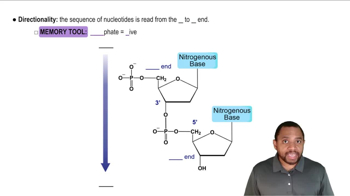
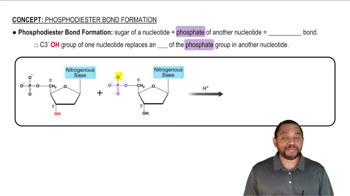
Provide the products for each of the following condensation reactions:
b.
What is the name of the bond that joins nucleotides in a nucleic acid?
Describe the differences in the two ends of a nucleic acid.
Describe the orientation of antiparallel strands in DNA. Use the terms 3' and 5' in your description.
How are the two strands of nucleic acid in DNA held together?
Write the base sequence and label the 3' and 5' ends of the complementary strand for a segment of DNA with the following base sequences:
b. 5'CCCCTTTT3'