Textbook Question
Draw the skeletal structure for each of the following compounds:
(a) 3-ethylhexane
1215
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Draw the skeletal structure for each of the following compounds:
(a) 3-ethylhexane
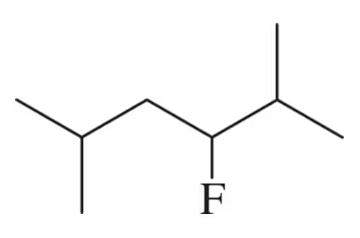
Give the correct IUPAC name for each of the following compounds:
(a)
Give the correct IUPAC name for each of the following compounds:
(c)
What is the difference between a conformational isomer of a compound and a structural isomer of the same compound?
Determine the relationship between each of the pairs of the following compounds. Are they structural isomers (different molecules), conformational isomers (the same molecule), or not related?
(b)
Determine the relationship between each of the pairs of the following compounds. Are they structural isomers (different molecules), conformational isomers (the same molecule), or not related?
(a)