CIA Problem 4.2 Draw the Lewis dot structures for the molecules CO and NO. What is different about these structures compared with the general examples we have seen so far? How could these Lewis structures provide insight into the high chemical reactivity of these molecules?
Ch.4 Molecular Compounds

Chapter 4, Problem 3
What are likely formulas for the following molecules?
a. CH2Cl?
b. BH?
c. NI?
d. SiCl?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the problem. The question asks for the likely molecular formulas for the given molecules. This involves determining the number of atoms of each element in the molecule based on chemical bonding rules and the octet rule (or duet rule for hydrogen).
Step 2: Analyze part (a) CH₂Clɂ. Carbon typically forms four bonds to satisfy the octet rule. Hydrogen forms one bond, and chlorine forms one bond. To complete the structure, determine how many hydrogens and chlorines are needed to satisfy carbon's four bonds.
Step 3: Analyze part (b) BHɂ. Boron typically forms three bonds because it has three valence electrons. Hydrogen forms one bond. Determine how many hydrogens are needed to satisfy boron's bonding capacity.
Step 4: Analyze part (c) NIɂ. Nitrogen typically forms three bonds to satisfy the octet rule, and iodine typically forms one bond. Determine how many iodines are needed to satisfy nitrogen's bonding capacity.
Step 5: Analyze part (d) SiClɂ. Silicon, like carbon, typically forms four bonds to satisfy the octet rule. Chlorine forms one bond. Determine how many chlorines are needed to satisfy silicon's bonding capacity.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
8mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Formulas
A molecular formula represents the number and types of atoms in a molecule. It is expressed using chemical symbols and subscripts, indicating how many of each atom are present. For example, in CH₂Cl₂, 'C' stands for carbon, 'H' for hydrogen, and 'Cl' for chlorine, with subscripts showing the quantity of each atom.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molecular Formula
Valency and Bonding
Valency refers to the ability of an atom to bond with other atoms, determined by the number of electrons in its outer shell. Understanding valency is crucial for predicting how atoms combine to form molecules. For instance, carbon typically has a valency of four, allowing it to form four bonds, while chlorine has a valency of one.
Recommended video:
Guided course
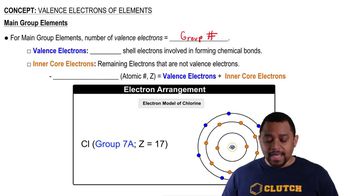
Valence Electrons of Elements (Simplified) Concept 1
Common Chemical Notation
Chemical notation is a system of symbols used to represent chemical substances and their interactions. It includes not only molecular formulas but also structural formulas that depict how atoms are arranged. Familiarity with this notation helps in interpreting and writing chemical equations accurately, which is essential for identifying molecular formulas.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Scientific Notation
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1532
views
Textbook Question
How many covalent bonds are formed by each atom in the following molecules? Draw molecules using the electron-dot-symbols and lines to show the covalent bonds.
a. PH3
b. H2Se
c. HCl
d. SiF
1730
views
Textbook Question
What is a coordinate covalent bond, and how does it differ from a covalent bond?
2160
views
Textbook Question
Identify the bonds formed between the following pairs of atoms as either covalent or ionic.
d. Zinc and fluorine
1809
views
Textbook Question
Write electron-dot symbols to show the number of covalent bonds and the lone pairs of electrons in the molecules that are formed by reactions between the atoms in Problem 4.34.
a. Aluminum and bromine
b. Carbon and fluorine
c. Cesium and iodine
d. Zinc and fluorine
e. Lithium and chlorine
1678
views
