The following diagrams represent two similar reactions that have achieved equilibrium:
<IMAGE>
a. Write the expression for the equilibrium constant for each reaction.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
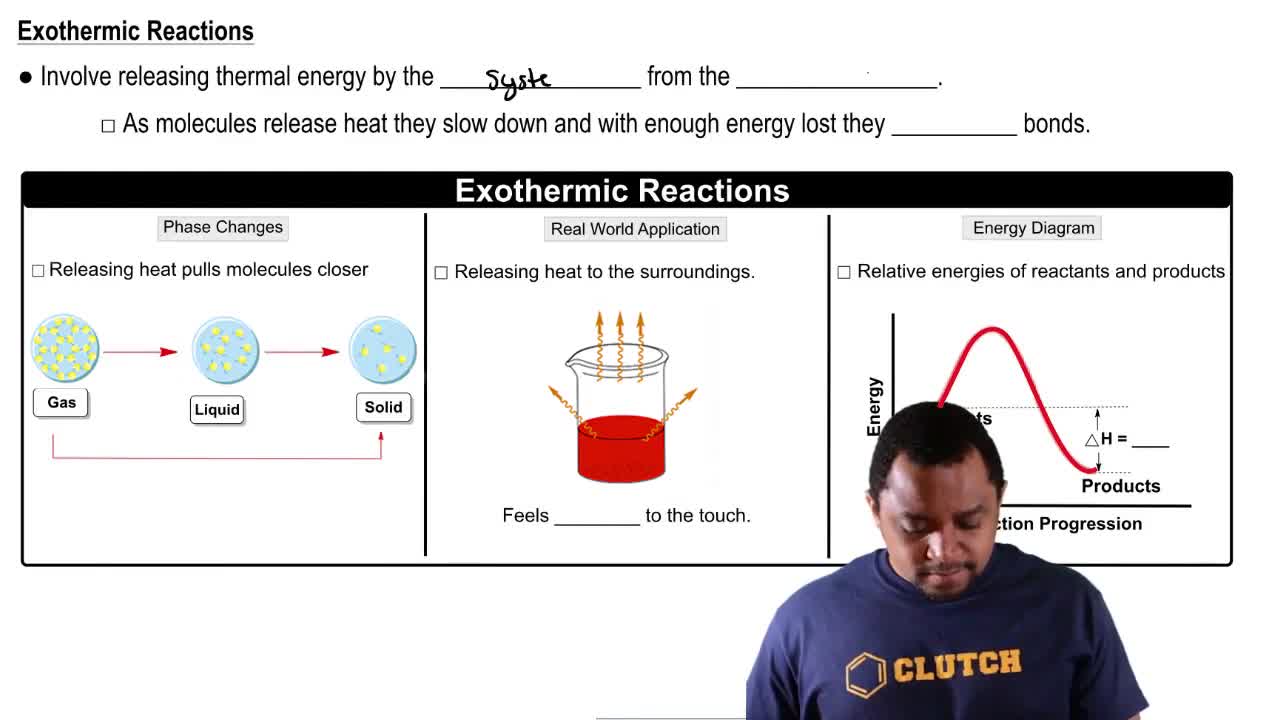

The following diagrams represent two similar reactions that have achieved equilibrium:
<IMAGE>
a. Write the expression for the equilibrium constant for each reaction.
The following diagrams represent two similar reactions that have achieved equilibrium:
<IMAGE>
b. Calculate the value for the equilibrium constant for each reaction.
Is the yield of SO3 at equilibrium favored by a higher or lower pressure? By a higher or lower temperature?
2 SO2(g) + O2 ⇌ 2 SO3(g) ∆H = -47 kcal/mol
What effect do the listed changes have on the position of the equilibrium in the reaction of carbon with hydrogen?
C(s) + 2 H2(g) ⇌ CH4(g) ∆H = -18 kcal/mol (-75kJ/mol)
b. Increasing pressure by decreasing volume
What effect do the listed changes have on the position of the equilibrium in the reaction of carbon with hydrogen?
C(s) + 2 H2(g) ⇌ CH4(g) ∆H = -18 kcal/mol (-75kJ/mol)
c. Allowing CH4 to escape continuously from the reaction vessel
Two curves are shown in the following energy diagram:
b. Which curve represents the spontaneous reaction, and which the nonspontaneous?