Textbook Question
For each of the following, give an example of a member compound containing 5 carbons total:
(a) Alcohol
1350
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
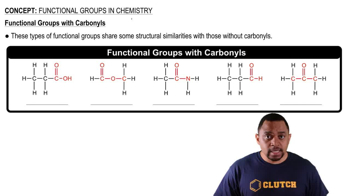


For each of the following, give an example of a member compound containing 5 carbons total:
(a) Alcohol
For each of the following, give an example of a member compound containing 5 carbons total:
(d) Ether
Identify the functional groups in the following molecules:
(b)
Propose structures for molecules that fit the following descriptions:
(c) A compound with the formula C3H7NOS that is both an amide and a thiol
Propose structures for molecules that fit the following descriptions:
(c) An aromatic compound that is also an ether, C8H10O
If one compound has the formula C5H10 and another has the formula C4H10 are the two compounds isomers? Explain.