Textbook Question
For each of the following, give an example of a member compound containing 5 carbons total:
(d) Ether
1228
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

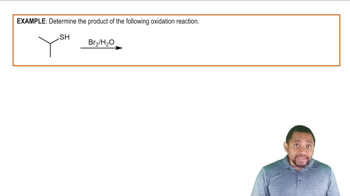

For each of the following, give an example of a member compound containing 5 carbons total:
(d) Ether
Identify the functional groups in the following molecules:
(b)
Propose structures for molecules that fit the following descriptions:
(b) An ester with the formula C6H12O2
Propose structures for molecules that fit the following descriptions:
(c) An aromatic compound that is also an ether, C8H10O
If one compound has the formula C5H10 and another has the formula C4H10 are the two compounds isomers? Explain.
Give an example of a compound that meets the following descriptions:
b. A cycloalkane with three substituents