Textbook Question
Draw and name all phenols with the formula C7H8O .
1737
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
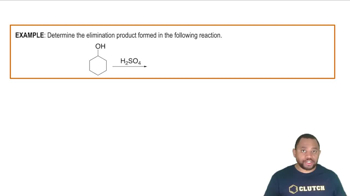

Draw and name all phenols with the formula C7H8O .
When ethylbenzene is reacted with nitric acid, three possible benzenes containing both a nitro group and an ethyl group are obtained. Draw and name them.
If bromocyclohexane were converted into cyclohexene, what kind of reaction would that be?
Identify the type of reaction for the following:
a.
b.
What alkene could you use to make the following products? Draw the structure of the alkene, and tell what other reagent is also required for the reaction to occur.
a.