Textbook Question
Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
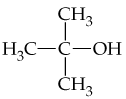
c. Phenyl tert-butyl ether
1068
views

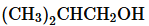
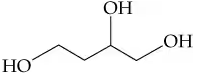
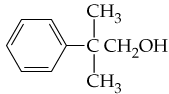
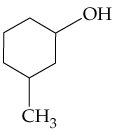
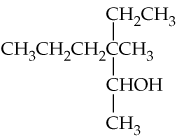
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
c. Phenyl tert-butyl ether
Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
e. 2,4-Dimethoxy-3-methylpentane
Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
f. 3-Methoxy-4-methyl-1-pentene
Arrange the following 6-carbon compounds in order of their expected boiling points, and explain your ranking:
a. Hexane
b. 1-Hexanol
c. Dipropyl ether (CH3CH2CH2—O—CH2CH2CH3)
Draw the structures of the aldehydes that might be oxidized to yield the following carboxylic acids:
c. CH3CH=CHCOOH
What type of product is formed on reaction of an alcohol with Na metal?