Assume that you have samples of the following two compounds, both with formula C7H8O. Both compounds dissolve in ether, but only one of the two dissolves in aqueous NaOH. How could you use this information to distinguish between them?

What alcohols would you oxidize to obtain the following carbonyl compounds?
a. 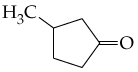
b. 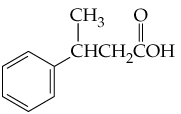
c. 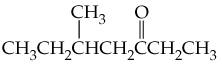
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Oxidation of Alcohols
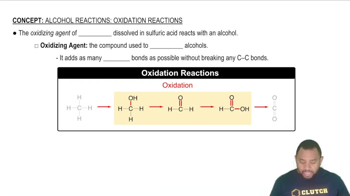
Types of Alcohols

Carbonyl Compounds

Which of the following alcohols can undergo oxidation? Draw the line structure of the product expected for those that can. Assume an excess of oxidizing agent is present.
a.
b.
c.
The following alkenes can be prepared by dehydration of an appropriate alcohol. Show the structure of the alcohol in each case that would provide the alkene shown as the major product.
e. 1,4-Pentadiene
What is the structural relationship between a thiol and an alcohol?
Oxidation of a dithiol such as 2,5-hexanedithiol forms a six-membered ring containing a disulfide group as part of the ring. Draw the structure of this cyclic disulfide (Hint: Draw the starting compound in line structure format first).
The boiling point of propanol is 97 °C ,much higher than that of either ethanethiol (37 °C) or chloroethane (13 °C) , even though all three compounds have similar MWs. Explain.
