Textbook Question
Draw structures corresponding to the following aldehyde and ketone names:
b. 4-Ethyl-2-isopropylhexanal
771
views

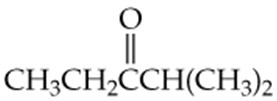
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Draw structures corresponding to the following aldehyde and ketone names:
b. 4-Ethyl-2-isopropylhexanal
Draw structures corresponding to the following aldehyde and ketone names:
e. 1,1,1-Trichloro-3-pentanone
Give systematic names for the following aldehydes and ketones:
a.
The following names are incorrect. What is wrong with each?
a. 1-Pentanone
The following names are incorrect. What is wrong with each?
b. 2-Butanal
Which of the following compounds will react with Tollens' reagent? With Benedict's reagent?
a. Cyclopentanon
b. Hexanal
c.