Textbook Question
Complete the following equations:
a.
1274
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
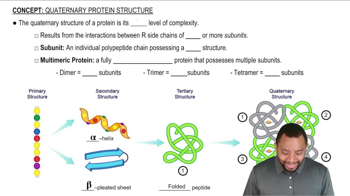


Complete the following equations:
a.
Complete the following equations:
c.
Which is the stronger base in each pair?
a. Ammonia or ethylamine
b.Triethylamine or pyridine
Write the structure of benzylamine hydrochloride in two different ways, and name the hydrochloride as an ammonium salt.
a. For the compound above, identify each nitrogen as either a primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary, or aromatic amine.
The structure of the amino acid lysine (in its uncharged form) is shown below.
a. Which amine groups would be able to participate in hydrogen bonding?