Textbook Question
Provide compounds that fit the following descriptions:
a. Two amines that are gases at room temperature
b. A heterocyclic amine
c. A compound with an amine group on an aromatic ring
841
views

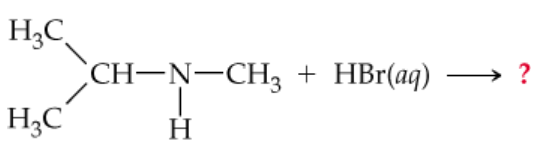
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Provide compounds that fit the following descriptions:
a. Two amines that are gases at room temperature
b. A heterocyclic amine
c. A compound with an amine group on an aromatic ring
Which of the following compounds are heterocyclic nitrogen compounds?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Write an equation for the acid-base equilibrium of:
a.Pyrrolidine and water
Label each species in the equilibrium as either an acid or a base.
Complete the following equations:
c.
Which is the stronger base in each pair?
a. Ammonia or ethylamine
b.Triethylamine or pyridine
Write the structures of the following compounds:
a. Butyldiethylammonium bromide