Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
a. 3-Methylpentanamide

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
a. 3-Methylpentanamide
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
b. N-Phenylacetamide
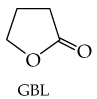
When both the carboxylic acid and the amine are in the same molecule, amide formation produces lactams. A lactam is a cyclic amide, where the amide group is part of the ring. Draw the structure of the product(s) obtained from acid hydrolysis of these lactams.
a.
Household soap is a mixture of the sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids that arise from saponification of animal fat.
b. Draw the structures of the soap molecules produced in the following reaction:
A simple polyamide can be made from ethylenediamine and oxalic acid (Table 17.1). Draw the polymer formed when three units of ethylenediamine reacts with two units of oxalic acid.