Textbook Question
Write the formulas of potassium salicylate and disodium oxalate.
507
views

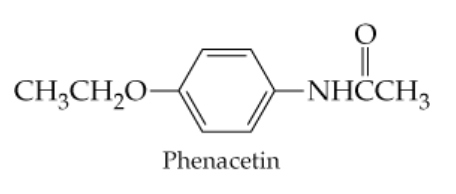
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Write the formulas of potassium salicylate and disodium oxalate.
Draw structures of the amides that can be made from the following reactants:
a. CH3NH2 + (CH3)2CHCOOH →?
Draw structures of the amides that can be made from the following reactants:
b.
Draw the products you would obtain from acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the following esters.
a. Isopropyl benzoate
Draw the products you would obtain from acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the following esters.
b.
What carboxylic acids and amines result from hydrolysis of the following amides?
a.