Is serine chiral? Draw serine and identify the chiral atom. Explain why serine is chiral.

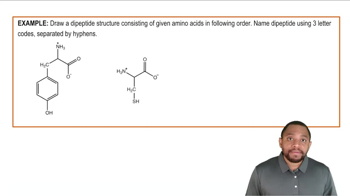
Valine is an amino acid with a nonpolar side chain, and serine is an amino acid with a polar side chain. Draw the two dipeptides that can be formed by these two amino acids. Identify the peptide bond.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Amino Acids

Dipeptides
Peptide Bond
Two of the 20 common amino acids have two chiral carbon atoms in their structures. Identify these amino acids and their chiral carbon atoms.
Draw the structure of glutamic acid at low pH, at high pH, and at the two forms that exist between low pH and high pH. Which of these structures represents the zwitterion?
Tripeptides are composed of three amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Given a set of amino acids, you can make several different tripeptides.
a. Use the three-letter shorthand notations to name all the tripeptides that can be made from serine, tyrosine, and glycine. Each amino acid will be used once in each tripeptide.
Using three-letter abbreviations, show the six tripeptides that contain isoleucine, arginine, and valine.
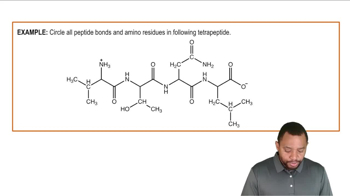
Identify the amino acids in the following dipeptide and tripeptide, and write the abbreviated forms of the peptide names. Copy the dipeptides, draw a box around the peptide bonds, and use an arrow to identify the α-carbon atoms. Draw a circle around the R groups, and indicate if the R groups are neutral, polar, acidic, or basic.
a.
