Compare and contrast the characteristics of fibrous and globular proteins. Consider biological function, water solubility, amino acid composition, secondary structure, and tertiary structure. Give examples of three fibrous and three globular proteins. (Hint: Make a table.)

Name four biological functions of proteins in the human body, and give an example of a protein for each function.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Enzymatic Function

Structural Support

Transport Function
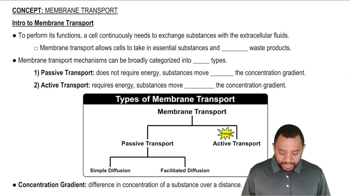
Cell membranes are studded with proteins. Some of these proteins, involved in the transport of molecules across the membrane into the cell, span the entire membrane and are called transmembrane proteins. The interior of the cell membrane is hydrophobic and nonpolar, whereas both the extracellular and intracellular fluids are water-based.
a. List three amino acids you would expect to find in the part of a transmembrane protein that lies within the cell membrane.
Threonine has two chiral centers. Draw L-threonine and indicate which carbon atoms are chiral. Which carbon atom is responsible for D and L configuration?
What kind of biological function would each of the following proteins perform?
a. Human growth hormone
What kind of biological function would each of the following proteins perform?
c. Protease
What amino acids do the following abbreviations stand for? Draw the structure of each.
a. Val
