Fresh pineapple cannot be used in gelatin desserts because it contains an enzyme that hydrolyzes the proteins in gelatin, destroying the gelling action. Canned pineapple can be added to gelatin with no problem. Why?

Oxytocin is a small peptide that is used to induce labor by causing contractions in uterine walls. It has the primary structure Cys-Tyr-Ile-Gln-Asn-Cys-Pro-Leu-Gln. This peptide is held in a cyclic configuration by a disulfide bridge. Draw a diagram of oxytocin, showing the disulfide bridge.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
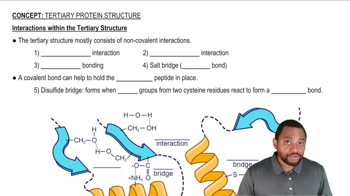
Key Concepts
Oxytocin Structure

Disulfide Bridge
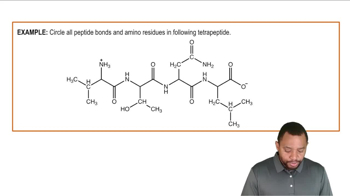
Peptide Diagramming
As a chef, you prepare a wide variety of foods daily. The following dishes all contain protein. What method (if any) has been used to denature the protein present in each food?
a. Charcoal-grilled steak
For each amino acid listed, tell whether its influence on tertiary structure is largely through hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonding, formation of salt bridges, covalent bonding, or some combination of these effects.
a. Tyrosine
Four of the most abundant amino acids in proteins are leucine, alanine, glycine, and valine. What do these amino acids have in common? Would you expect these amino acids to be found on the interior or on the exterior of the protein?
Globular proteins are water-soluble, whereas fibrous proteins are insoluble in water. Indicate whether you expect the following amino acids to be on the surface of a globular protein or on the surface of a fibrous protein.
a. Ala
A family visits a pediatrician with their sick child. The four-month-old baby is pale, has obvious episodes of pain, and is not thriving. The doctor orders a series of blood tests, including a test for hemoglobin types. The results show that the infant is not only anemic but that the anemia is due to sickle-cell anemia. The family wants to know if their other two children have sickle-cell anemia, sickle-cell trait, or no sickle-cell gene at all.
a. What test will be used?
