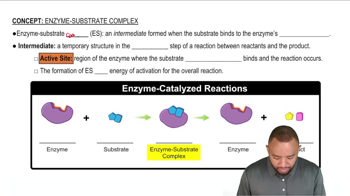
Textbook Question
The cofactors NAD+, Cu2+, Zn2+, coenzyme A, FAD, and Ni2+ are all needed by your body for enzymatic reactions.
a. Which cofactors are coenzymes?
1472
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

The cofactors NAD+, Cu2+, Zn2+, coenzyme A, FAD, and Ni2+ are all needed by your body for enzymatic reactions.
a. Which cofactors are coenzymes?
Describe the reactions that you would expect these enzymes to catalyze.
b. Aspartate transaminase
Identify and describe the chemical change in the lyase-catalyzed reaction in Table 19.4 that involves fumarate and malate. Identify the substrate(s) and product(s).
Which of the following reactions can be catalyzed by a decarboxylase?
a.
b.
What do we mean when we say an enzyme is saturated with substrate? When an enzyme is saturated with substrate, how does adding more (a) substrate and (b) enzyme affect the rate of the reaction?