Textbook Question
Name an enzyme that acts on each molecule.
c. DNA
1726
views

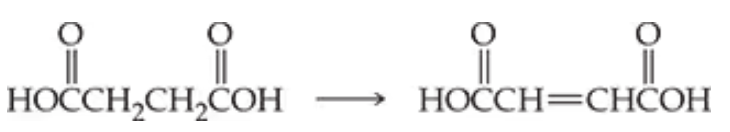
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Name an enzyme that acts on each molecule.
c. DNA
Name an enzyme that acts on each molecule.
a. Lactose
Name an enzyme that acts on each molecule.
c. RNA
What kind of reaction does each of these enzymes catalyze?
b. A transmethylase
What kind of reaction does each of these enzymes catalyze?
c. A reductase
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) catalyzes the following reaction. To what class of enzymes does ADH belong?