A common metabolic strategy is the lack of reactivity—that is, the slowness to react—of compounds whose breakdown is exergonic. For example, hydrolysis of ATP to ADP or adenosine monophosphate (AMP) is exergonic but does not take place without an appropriate enzyme present. Why would the cell use this metabolic strategy?

Which of the following is found in the coenzyme FAD?
a. Two heterocyclic rings
b. ADP
c. A substituted benzene ring
d. A phosphate anhydride bond
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
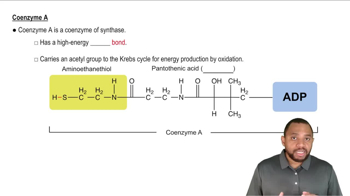
Coenzymes
Structure of FAD

Heterocyclic Rings

One of the steps in lipid metabolism is the reaction of glycerol (1,2,3-propanetriol, HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH, with ATP to yield glycerol 1-phosphate. Write the equation for this reaction using the curved arrow symbolism.
The hydrolysis of acetyl phosphate to give acetate and hydrogen phosphate ion has ∆G = -10.3 kcal/mol (-43.1 kJ/mol). Combine the equations and ∆G values to determine whether coupling of this reaction with phosphorylation of ADP to produce ATP is favorable. (You need give only compound names or abbreviations in the equations.)
Look ahead to Figure 21.8 for the citric acid cycle.
<IMAGE>
a. Draw the structures of the reactants in steps 3, 6, and 8, and indicate which hydrogen atoms are removed in these reactions.
Look ahead to Figure 21.8 for the citric acid cycle.
<IMAGE>
b. What class of enzymes carry out these reactions?
Why, do you suppose, the coenzyme for the reaction in the citric acid cycle that is catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase is FAD and not NAD+?
