Textbook Question
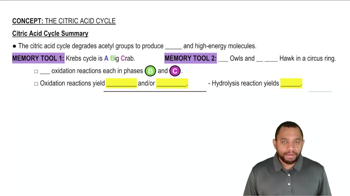
Look at the eight steps of the citric acid cycle (Figure 21.8) and answer the following questions:
b. Which steps involve decarboxylation (loss of CO2)?
507
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Look at the eight steps of the citric acid cycle (Figure 21.8) and answer the following questions:
b. Which steps involve decarboxylation (loss of CO2)?
Look at the eight steps of the citric acid cycle (Figure 21.8) and answer the following questions:
c. Which step or steps involve a hydration reaction?
How many NADH and how many FADH2 molecules are formed in the citric acid cycle?
Which reactions of the citric acid cycle transfer energy as NADH?
What are the two primary functions of the electron-transport chain?
What two coenzymes are involved with initial events of the electron-transport chain?