Textbook Question
Which reactions of the citric acid cycle transfer energy as FADH2?
1392
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
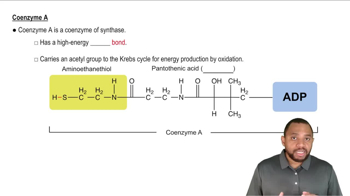
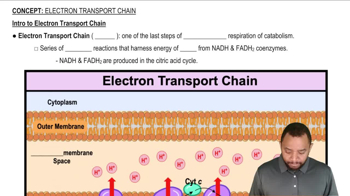
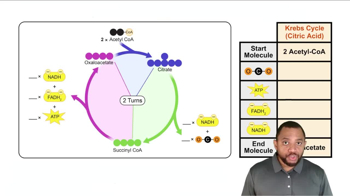
Which reactions of the citric acid cycle transfer energy as FADH2?
Which reactions of the citric acid cycle transfer energy as NADH?
What are the two primary functions of the electron-transport chain?
What are the ultimate products of the electron-transport chain?
What do the following abbreviations stand for?
b. CoQ
What do the following abbreviations stand for?
c. NADH/H+