Textbook Question
In oxidative phosphorylation, what is oxidized and what is phosphorylated?
1536
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

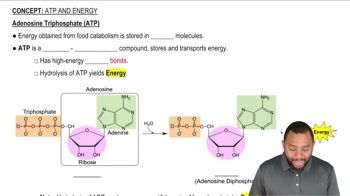
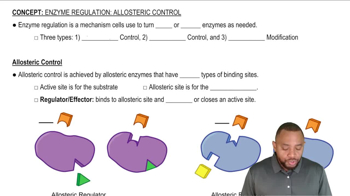
In oxidative phosphorylation, what is oxidized and what is phosphorylated?
Oxidative phosphorylation has three reaction products.
a. What is the energy-carrying product?
What supplies the energy to drive oxidative phosphorylation?
With what class of enzymes are the coenzymes NAD+ and FAD associated?
We talk of burning food in a combustion process, producing CO2 and H2O from food and O2. Explain how O2 is involved in the process although no O2 is directly involved in the citric acid cycle.
If you use a flame to burn a pile of glucose completely to give carbon dioxide and water, the overall reaction is identical to the metabolic oxidation of glucose. Explain the differences in the fate of the energy released in each case.