Textbook Question
Why must the breakdown of molecules for energy in the body occur in several steps, rather than in one step?
598
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


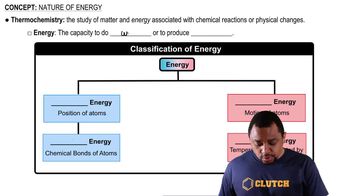
Why must the breakdown of molecules for energy in the body occur in several steps, rather than in one step?
With what class of enzymes are the coenzymes NAD+ and FAD associated?
We talk of burning food in a combustion process, producing CO2 and H2O from food and O2. Explain how O2 is involved in the process although no O2 is directly involved in the citric acid cycle.
The mitochondrion pumps H+ from the matrix into the intermembrane space. Which region is more acidic, the matrix or the intermembrane space? Why?
The citric acid cycle contains four 4-carbon dicarboxylic acids.
a. Name them.
The citric acid cycle contains four 4-carbon dicarboxylic acids.
b. Arrange them in order from least oxidized to most oxidized.